An IP camera, also known as a network camera, is a digital camera that can transmit and receive data over a network or the internet. Unlike traditional analog CCTV cameras, which require a physical connection to a recording device, IP cameras can be connected directly to a network, such as a router or a switch. They can transmit video and other data wirelessly or over a wired connection.
IP cameras typically have built-in web servers that allow users to access and control the camera remotely using a computer or mobile device. Some IP cameras also come with advanced features such as motion detection, night vision, and two-way audio, allowing users to communicate with anyone in the camera’s field of view.
IP cameras are widely used for security and surveillance in homes, businesses, and public spaces. They are available in various sizes and form factors, from compact dome cameras to large outdoor cameras with weatherproof housings.

Installing an IP camera involves several steps. Here is a general guide to follow:
- Choose the location: Select a suitable location for your IP camera. It should be placed in a location that provides a clear view of the area you want to monitor.
- Power source: Ensure that your IP camera is near a power source or that you have a power outlet nearby.
- Connect the camera to your network: Connect the IP camera to your network using an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. If you are using Wi-Fi, make sure the camera is within range of your wireless network.
- Configure the IP camera: Once the camera is connected to your network, use your computer or mobile device to configure the camera. You will need to enter the camera’s IP address into a web browser to access its settings page.
- Set up the camera: Follow the instructions provided in the camera’s manual to complete the setup process. You may need to create a username and password, set the time and date, and adjust other settings.
- Mount the camera: After the camera is set up, mount it in the desired location using the appropriate hardware. Make sure the camera is securely mounted and pointed in the direction you want to monitor.
- Test the camera: After mounting the camera, test it to ensure it is working properly. Check the camera’s live feed to make sure you can see the area you want to monitor.
- Monitor your camera: Once the camera is installed and working properly, you can monitor the area remotely using your computer or mobile device.
What is POE and why does it need to install?
POE stands for Power over Ethernet, and it is a technology that allows network cables to carry electrical power in addition to data. In the context of IP cameras, POE allows the camera to receive both power and data over a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for a separate power supply or electrical wiring.
Here are some of the reasons why POE is commonly used to install IP cameras:
- Simplified installation: POE eliminates the need for a separate power supply, making the installation process simpler and more efficient. It also reduces the amount of wiring required, which can save time and money.
- Greater flexibility: POE allows cameras to be installed in locations where electrical outlets are not available, such as ceilings or outdoor areas. This provides greater flexibility in terms of camera placement and reduces the need for additional infrastructure.
- Improved reliability: By using a single cable to transmit power and data, POE eliminates the need for separate power supplies, which can be a common point of failure in traditional installations. This can result in improved reliability and reduced downtime.
- Cost savings: POE can be a cost-effective solution for installations where power outlets are not readily available. It can also reduce the cost of installation by eliminating the need for separate wiring and power supplies.
In summary, POE is a convenient and cost-effective way to power and connect IP cameras, offering simplified installation, greater flexibility, improved reliability, and potential cost savings.
Why is Ethernet cable used in IP Cameras?
Ethernet cables are commonly used with IP cameras to provide both power and data transmission over a single cable. Ethernet cables are typically categorized based on their performance specifications, with Category 5 (Cat5) and Category 6 (Cat6) cables being the most commonly used.
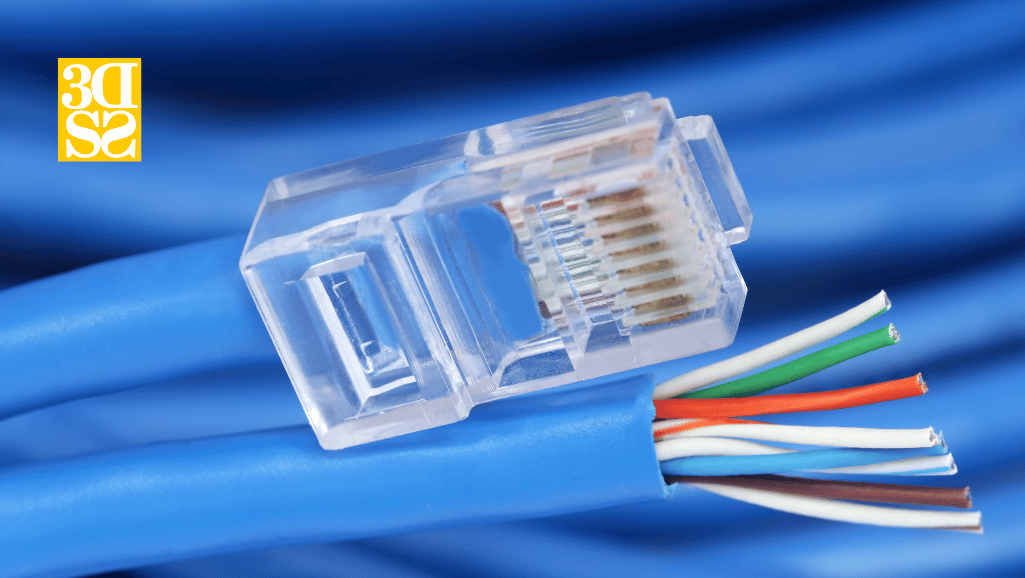
When using an Ethernet cable with an IP camera, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- PoE Support: If the camera supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), the Ethernet cable can be used to provide both power and data transmission over the same cable, eliminating the need for a separate power source. PoE requires a network switch or injector that supports the PoE standard.
- Cable Length: The length of the Ethernet cable used with an IP camera can impact the quality of the video and data transmission. It is important to use a cable that is appropriate for the distance between the camera and the network switch or injector.
- Cable Type: Cat5 and Cat6 cables are the most commonly used types of Ethernet cables for IP cameras. Cat5 cables can support data transmission speeds up to 100 Mbps, while Cat6 cables can support speeds up to 10 Gbps. It is important to use a cable that is appropriate for the speed and bandwidth requirements of the camera.
- Connector Type: Ethernet cables typically use RJ45 connectors, which are a standard type of connector for Ethernet cables. It is important to use connectors that are compatible with the camera and network switch or injector.
In summary, Ethernet cables are commonly used with IP cameras to provide power and data transmission over a single cable. It is important to use a cable that is appropriate for the distance, speed, and bandwidth requirements of the camera, and to ensure that the connectors are compatible with the camera and network switch or injector.
Different between IP Camera and AHD Camera ?
IP cameras and AHD (Analog High Definition) cameras are two different types of surveillance cameras that have distinct differences in their technology, features, and capabilities.
- Technology: IP cameras use digital technology to transmit video and data over a network, while AHD cameras use analog technology to transmit video over a coaxial cable.
- Video Quality: IP cameras typically offer higher video quality than AHD cameras, with resolutions ranging from standard definition to ultra-high definition. AHD cameras are typically limited to 1080p resolution.
- Network Connectivity: IP cameras can be connected to a network using Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi, allowing for remote access and monitoring. AHD cameras are typically limited to local viewing and recording.
- Scalability: IP cameras can be easily added or removed from a network, making it easy to scale the system up or down as needed. AHD cameras may require additional equipment or cabling to add or remove cameras.
- Features: IP cameras often come with advanced features such as motion detection, facial recognition, and analytics that can help automate and streamline security operations. AHD cameras typically have fewer features.
- Cost: IP cameras tend to be more expensive than AHD cameras, due to their advanced technology and features. AHD cameras are typically more cost-effective for smaller installations.
In summary, IP cameras offer higher video quality, network connectivity, scalability, and advanced features, but are typically more expensive than AHD cameras. AHD cameras are more cost-effective and simpler to install, but are limited in their video quality and network connectivity. The choice between IP and AHD cameras depends on the specific needs and requirements of the installation.